[ISO27000]

Executive Summary

Information security is a critical concern for organizations of all sizes in today’s digital world. The ISO27000 series of standards provides a comprehensive framework for implementing and maintaining an information security management system (ISMS). This article provides a detailed overview of the ISO27000 series, including its benefits, key components, and implementation considerations.
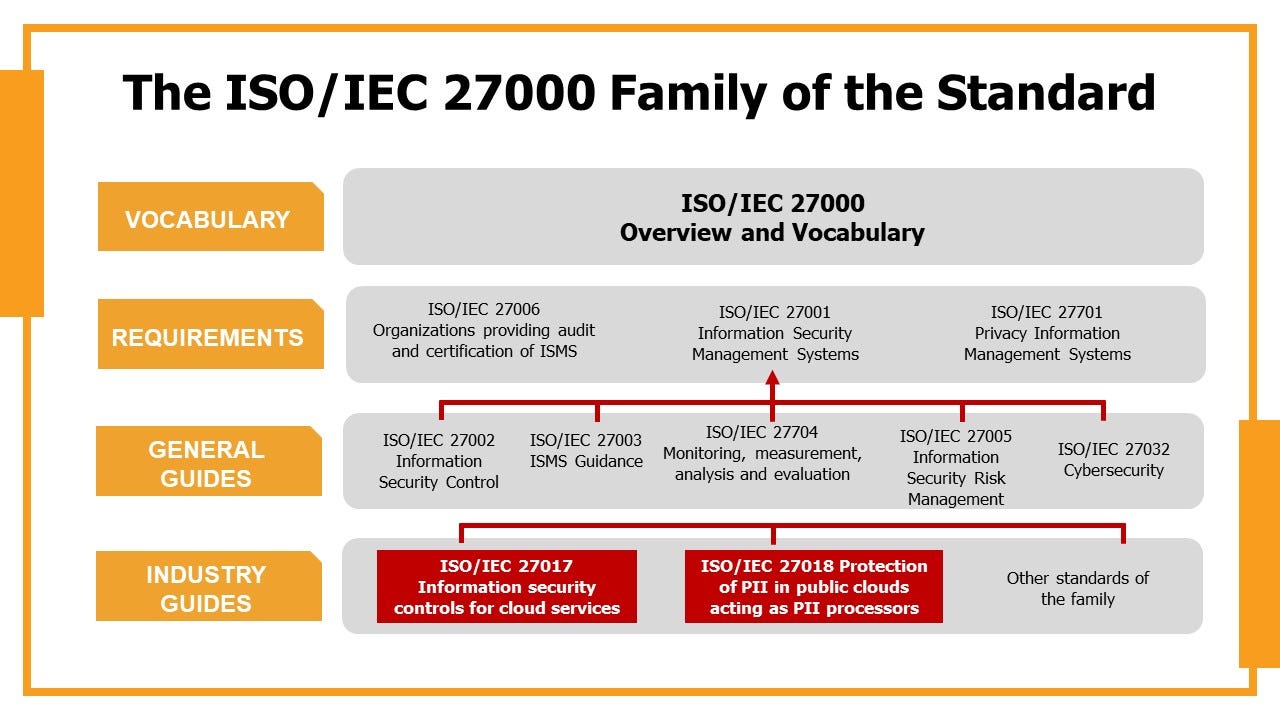
Introduction
The ISO27000 series is a collection of international standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to help organizations manage information security risks and protect their assets. It provides a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating information security threats, and it can be used by organizations of all sizes and industries.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of implementing ISO27000?
- Enhanced security: Reduces the risk of information security breaches and data loss.
- Improved compliance: Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
- Increased customer confidence: Demonstrates to customers that the organization is committed to protecting their information.
- Improved operational efficiency: Streamlines information security processes and improves coordination between departments.
- Reduced costs: Reduces the financial impact of information security breaches and compliance violations.
2. What are the key components of ISO27000?
- Risk assessment: Identifies and assesses potential information security risks.
- Information security policies: Defines the organization’s information security objectives and requirements.
- Information security controls: Implements measures to mitigate information security risks.
- Information security awareness and training: Ensures that employees are aware of information security risks and their responsibilities.
- Incident response planning: Establishes procedures for responding to information security incidents.
3. What are the considerations for implementing ISO27000?
- Scope and objectives: Clearly define the scope and objectives of the ISMS.
- Resources: Allocate sufficient resources for implementation and ongoing management.
- Stakeholder involvement: Engage key stakeholders in the implementation process.
- Continuous improvement: Establish a process for ongoing monitoring and improvement of the ISMS.
- Compliance mapping: Map the ISMS to relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Key Subtopics
1. Risk Assessment
- Asset inventory: Identify and classify all information assets within the scope of the ISMS.
- Threat identification: Identify potential threats to information security, including internal and external vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability assessment: Evaluate the likelihood and impact of potential threats on information assets.
- Risk analysis: Determine the overall risk level based on the likelihood and impact of threats and vulnerabilities.
- Risk treatment: Develop and implement measures to mitigate identified risks.
2. Information Security Policies
- Information security policy: Defines the overall information security objectives and requirements of the organization.
- Specific information security policies: Address specific aspects of information security, such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Asset classification: Classifies information assets based on their criticality and sensitivity.
- Access control: Defines rules and procedures for controlling access to information assets.
- Data protection: Protects information from unauthorized disclosure, modification, or destruction.
3. Information Security Controls
- Technical controls: Implement technology-based measures to mitigate information security risks, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Physical controls: Implement physical measures to protect information assets, such as access control systems, security cameras, and physical barriers.
- Administrative controls: Establish processes and procedures to manage information security risks, such as security awareness training, incident response plans, and backup and recovery procedures.
- Security monitoring: Continuously monitor information security systems and networks to detect and respond to threats.
- Vulnerability management: Patch and update systems and software to address identified vulnerabilities.
4. Information Security Awareness and Training
- Security awareness program: Educate employees about information security risks and their responsibilities.
- Training and development: Provide training to employees on information security policies and procedures.
- Simulation and testing: Conduct simulation and testing exercises to assess employees’ understanding of information security risks.
- Performance evaluation: Evaluate employees’ performance in meeting information security requirements.
- Continuous improvement: Update and refine security awareness and training programs to reflect changes in information security threats and risks.
5. Incident Response Planning
- Incident response plan: Establish a plan for responding to information security incidents.
- Incident detection: Define procedures for detecting and identifying information security incidents.
- Incident management: Establish procedures for managing information security incidents, including containment, investigation, and recovery.
- Incident recovery: Restore information systems and data to normal operation following an incident.
- Incident follow-up: Conduct a review of incidents to identify root causes and improve incident response procedures.
Conclusion
The ISO27000 series of standards provides organizations with a comprehensive framework for managing information security risks and protecting their assets. By implementing an ISMS based on ISO27000, organizations can enhance their security posture, improve compliance, and reduce the impact of information security breaches. The key to successful implementation lies in carefully considering the scope, objectives, and resources required, as well as ensuring ongoing monitoring and improvement of the ISMS.
Keyword Tags
- ISO27000
- Information Security
- Risk Assessment
- Security Controls
- Incident Response
