Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)

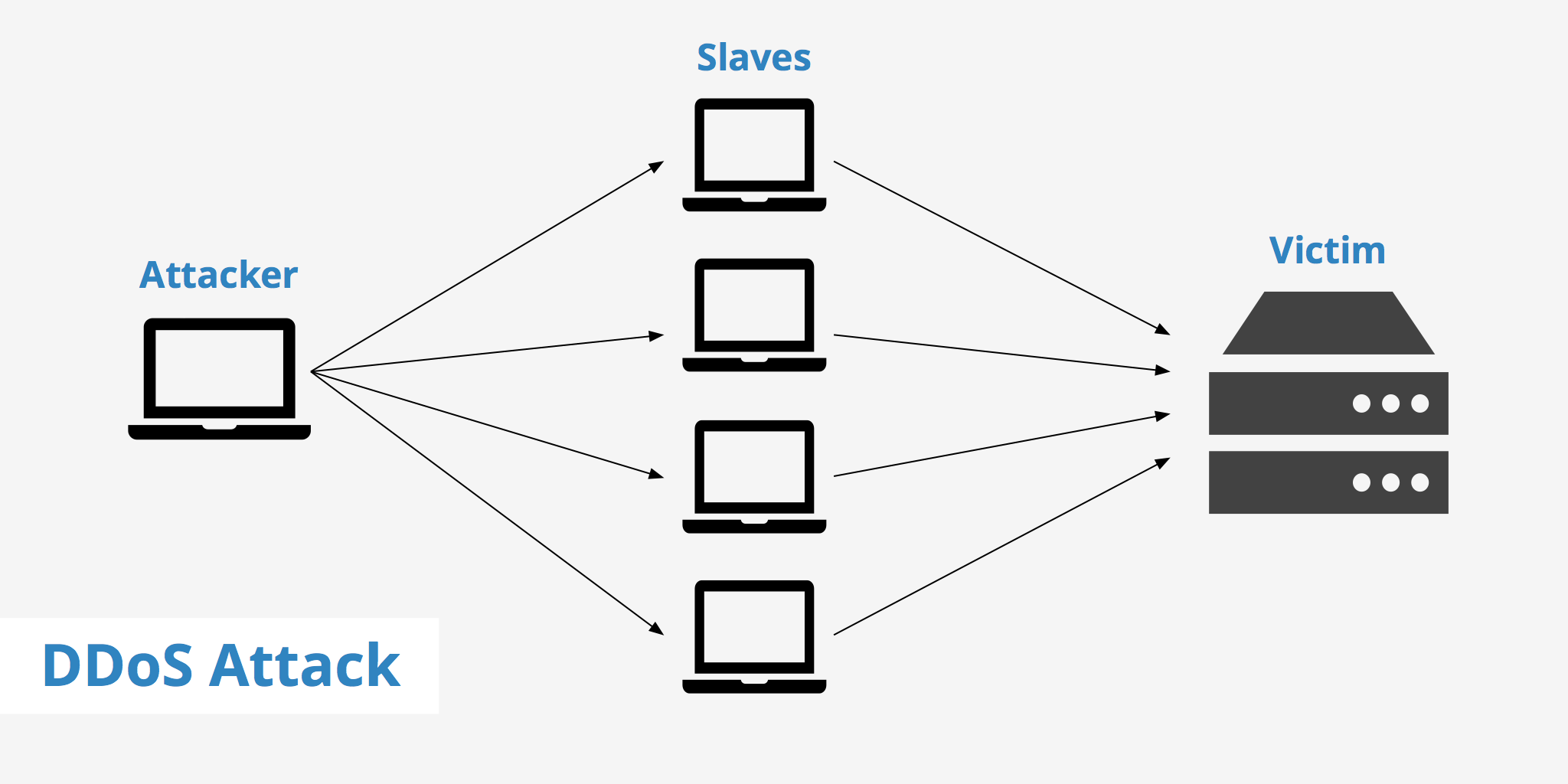
A DDoS attack is an attempt to overwhelm a target system with a flood of internet traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users. It is achieved by coordinating a network of compromised computers, known as a botnet, to simultaneously send a large number of requests to the target system. This overwhelming traffic can cause the target system to slow down or even crash, disrupting services such as websites, email, and online gaming.

Types of DDoS Attacks:
- Volume-based DDoS Attacks: These attacks flood the target system with a high volume of traffic, such as UDP packets or HTTP requests. The overwhelming number of requests can exhaust the target system’s resources and cause it to become unavailable.
- Protocol Attacks: These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols to exhaust the target system’s resources. For example, the SYN flood attack sends incomplete TCP connection requests to the target system, consuming its processing power until it becomes overwhelmed.
- Application-layer Attacks: These attacks target specific applications or services on the target system. They involve sending malicious traffic that exploits vulnerabilities in the application or its underlying infrastructure.
Impacts of DDoS Attacks:
- Website and Application Outages: DDoS attacks can cause websites and applications to become inaccessible, disrupting business operations, online transactions, and customer experience.
- Network Congestion: Overwhelming traffic from DDoS attacks can clog the target system’s network, affecting not only the target but also other systems on the same network.
- Data Loss and Corruption: Prolonged DDoS attacks can lead to data loss or corruption as the target system becomes overwhelmed and unable to process legitimate requests efficiently.
- Reputation Damage: Frequent or high-profile DDoS attacks can damage the reputation of the targeted organization, negatively impacting customer confidence and brand perception.
Mitigation of DDoS Attacks:
- Use DDoS Mitigation Services: Dedicated services can filter and absorb malicious traffic before it reaches the target system.
- Implement Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS can detect and alert on suspicious traffic, allowing network administrators to take action before an attack causes disruptions.
- Use Anti-DDoS Hardware: Specialized hardware appliances can be deployed to handle high volumes of traffic and mitigate DDoS attacks.
- Proactively Monitor Networks: Regular network monitoring can help identify potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by DDoS attackers.
